ESP 8266: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Stefan (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Stefan (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 111: | Zeile 111: | ||
https://www.mikrocontroller-elektronik.de/nodemcu-esp8266-tutorial-wlan-board-arduino-ide/ | https://www.mikrocontroller-elektronik.de/nodemcu-esp8266-tutorial-wlan-board-arduino-ide/ | ||
| − | == | + | == ESP Typen == |
=== Bluetooth Wifi ESP-32 Entwicklungs Board Modul Lora32 Lora 868Mhz Esp32 Lor M5J7 === | === Bluetooth Wifi ESP-32 Entwicklungs Board Modul Lora32 Lora 868Mhz Esp32 Lor M5J7 === | ||
[[Datei:ESP32 Lora 1.JPG]] | [[Datei:ESP32 Lora 1.JPG]] | ||
| Zeile 135: | Zeile 135: | ||
3) Achten Sie bei der Verwendung auf das Plus und Minus der Batterie, da diese sonst bescädigt wird. | 3) Achten Sie bei der Verwendung auf das Plus und Minus der Batterie, da diese sonst bescädigt wird. | ||
4) Beim Touchscreen-Eingangssignal des IO-Ports müssen Sie den 100nF-Pull-Down-Kondensator zu diesem Pin hinzufügen. | 4) Beim Touchscreen-Eingangssignal des IO-Ports müssen Sie den 100nF-Pull-Down-Kondensator zu diesem Pin hinzufügen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === ESP32 WIFI chip 0.96 inch OLED Bluetooth WIFI Kit CP2102 32M module for arduino === | ||
| + | [[Datei:ESP-WIFI-Kit.JPG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | WIFI Kit 8 is developed by our company cost-effective Internet of things development program, the main chip using ESP8266, with CP2014USB to serial chip, lithium battery interface and charge and discharge circuit, 32MByte Flash, WIFI antenna, 0.91-inch OLED display. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Can be programmed in Ard uino and NodeMCU environments. Operation is consistent with NodeMCU. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Leads all pins of ESP8266 | ||
| + | 12 digital pins can be configured to read, write, IIC, SPI, the middle, PWM and other functions | ||
| + | 1 AD input | ||
| + | Integrated 0.91-inch 128 * 32 OLED | ||
| + | Working voltage: 3.3V ~ 7V | ||
Version vom 2. Februar 2020, 14:28 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Einführung & Programmierung des ESP8266 NodeMCU Boards
- 2 ESP8266 Module - Starter Anleitung
- 3 Wiki
- 4 ESP Easy
- 5 Typen
- 6 GP2Y10
- 7 ESP Easy Sensoren in FHEM einbinden
- 8 Tinkerblog : ESP2866 & ESPEasy
- 9 ESPEASY PN532
- 10 Statusdisplay mit ESP Easy, DLCD und FHEM
- 11 Fhem: LCD 2004 Display mit ESPEasy als Statusanzeige
- 12 ArduiTouch Wandgehäuse Set für ESP8266 und ESP32
- 13 NodeMCU und ESP8266 – Einstieg in die Programmierung
- 14 ESP Typen
Einführung & Programmierung des ESP8266 NodeMCU Boards
https://tutorials-raspberrypi.de/einfuehrung-programmierung-esp8266-nodemcu-boards/
ESP8266 Module - Starter Anleitung
http://stefanfrings.de/esp8266/index.html
Wiki
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/ESP8266
ESP Easy
Get started Getting started with the ESP Easy takes a few basic steps. In most cases your ESP module comes with the AT firmware or the NodeMCU LUA firmware. We need to replace the existing Firmware with the ESP Easy firmware. We provide a (Windows only) flashtool to make this process an easy job. Below you find the general flow of this but an in depth guide is found here. 1. Download firmware as binary including flash tool 2. Connect the ESP to Windows PC Using either USB/UART of board or separate USB/TTL adapter 3. Write firmware using flash tool Note necessity for GPIO to be LOW to enter flashmode 4. Restart ESP. WiFi AP "ESP_Easy_0" will appear, password: configesp (prior to 2.0 the AP was named ESP_0) If you're not automatically taken to the log-in page, browse to 192.168.4.1 5. Search for you routers WiFi and connect (if you have multiple AP they will all show up with the same SSID name multiple times) 6. Reconnect to your WiFi and enter IP adress shown on previous screen
https://www.letscontrolit.com
https://www.letscontrolit.com/wiki/index.php/ESPEasy
https://github.com/letscontrolit/ESPEasy/releases
https://www.letscontrolit.com/wiki/index.php/History_of_ESP_Easy
the AP was named ESP_0). Connect to this access point with default password: configesp.
ESP Easy – Weboberfläche zur Konfiguration von ESP8266-Chips
https://waschto.eu/easyesp
GitHub
https://github.com/letscontrolit/ESPEasy/releases
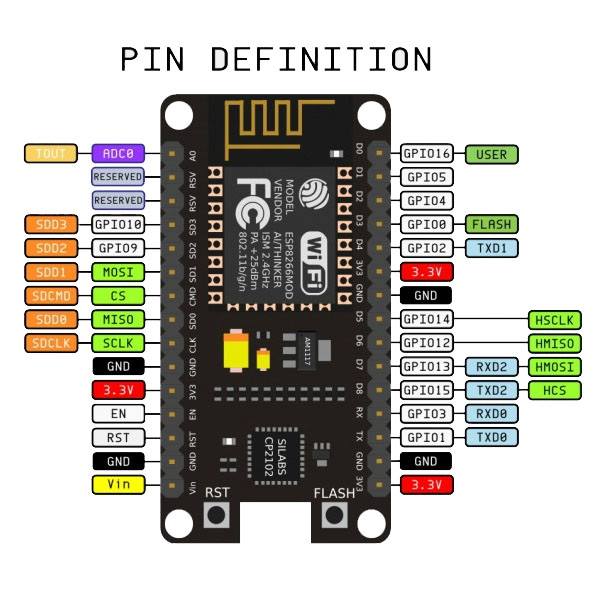
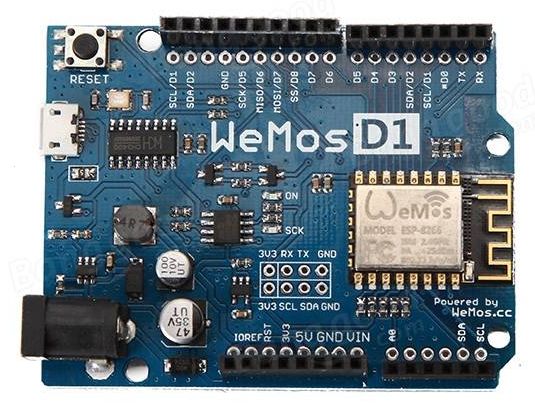
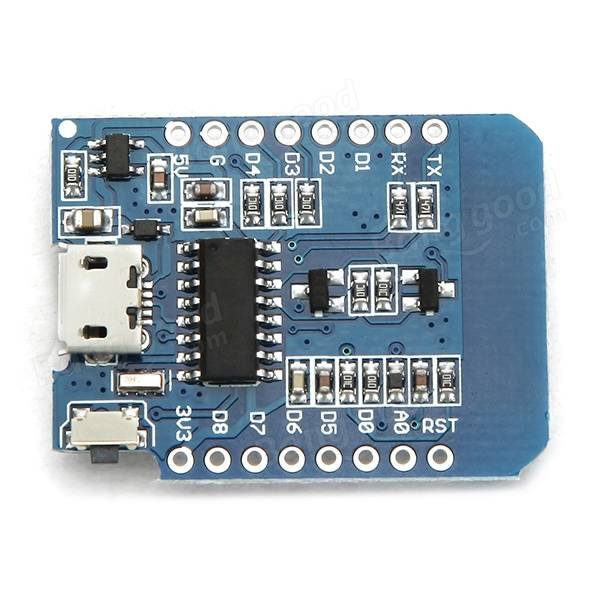
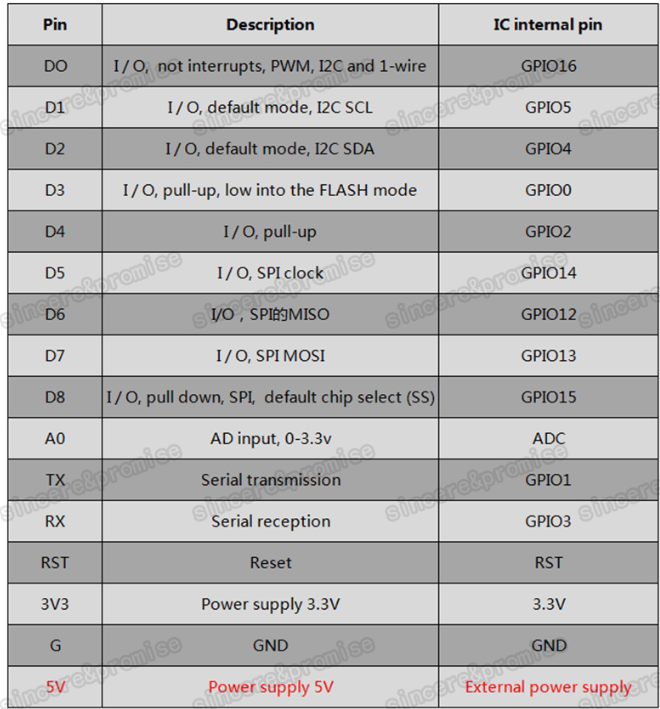
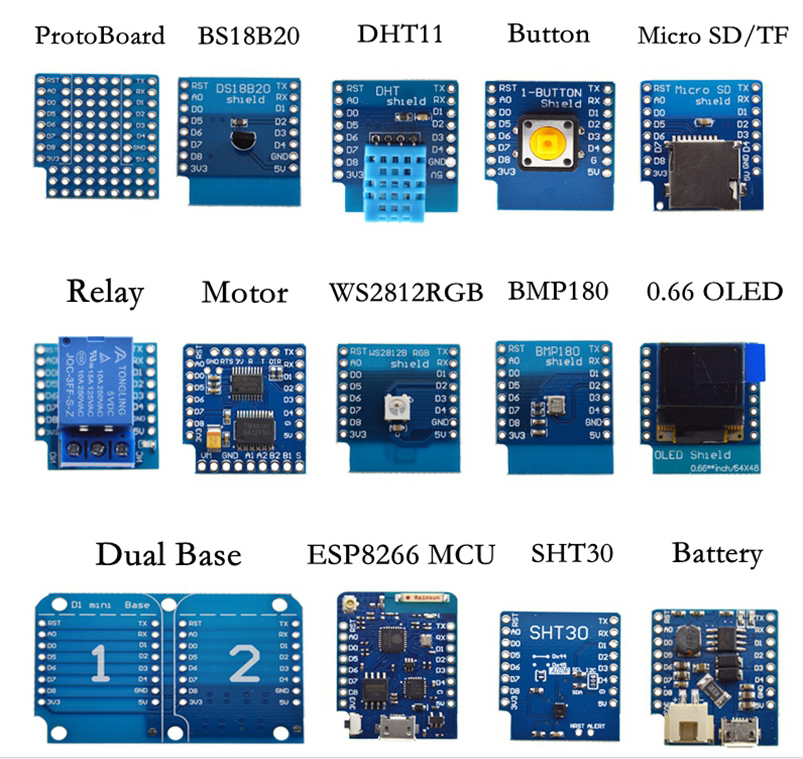
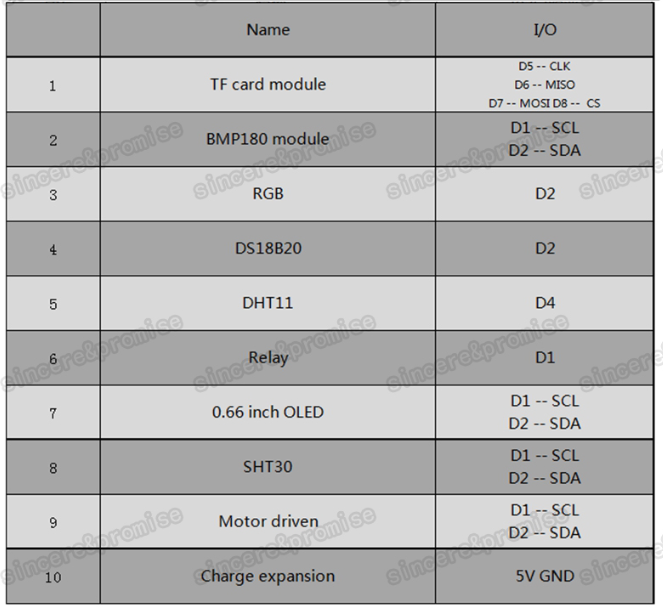
Typen
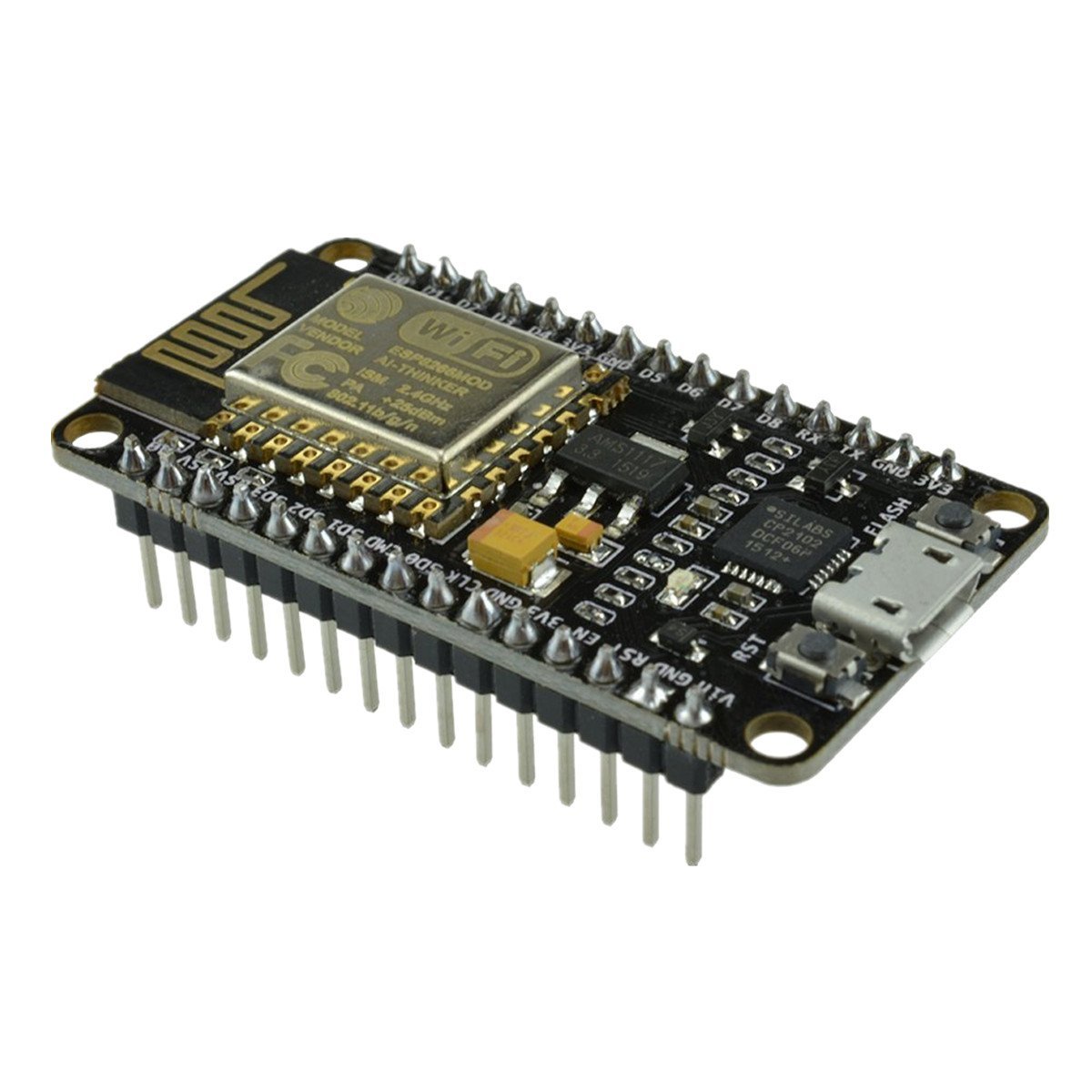
NodeMCU
QuickStart
https://benlo.com/esp8266/esp8266QuickStart.html http://theelectromania.blogspot.de/2016/02/how-to-program-esp8266-esp-12e-nodemcu.html
Wemos D1
Wemos D1 Mini
Boards
D1 Mini Pro
Battery Board
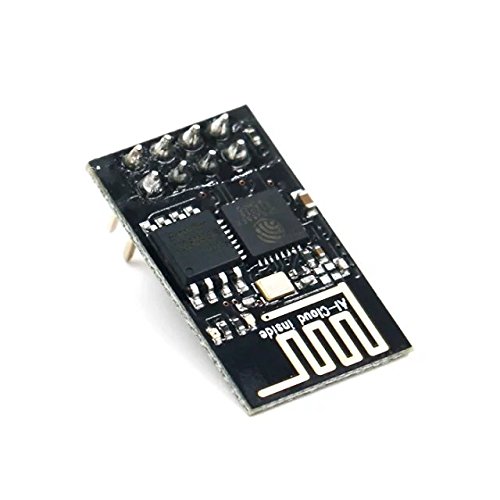
ESP 01
ESP 07
ESP 12
GP2Y10
https://www.letscontrolit.com/wiki/index.php/GP2Y10
ESP Easy Sensoren in FHEM einbinden
https://waschto.eu/easyesp-sensoren-in-fhem-einbinden
Tinkerblog : ESP2866 & ESPEasy
https://tinkerblog.net/wemos-d1-mini-node-mcu-esp-easy/
ESPEASY PN532
https://www.letscontrolit.com/wiki/index.php/PN532
Statusdisplay mit ESP Easy, DLCD und FHEM
https://waschto.eu/statusdisplay-mit-esp-easy-dlcd-und-fhem/
Fhem: LCD 2004 Display mit ESPEasy als Statusanzeige
https://blog.moneybag.de/fhem-lcd-2004-display-mit-espeasy-als-statusanzeige/
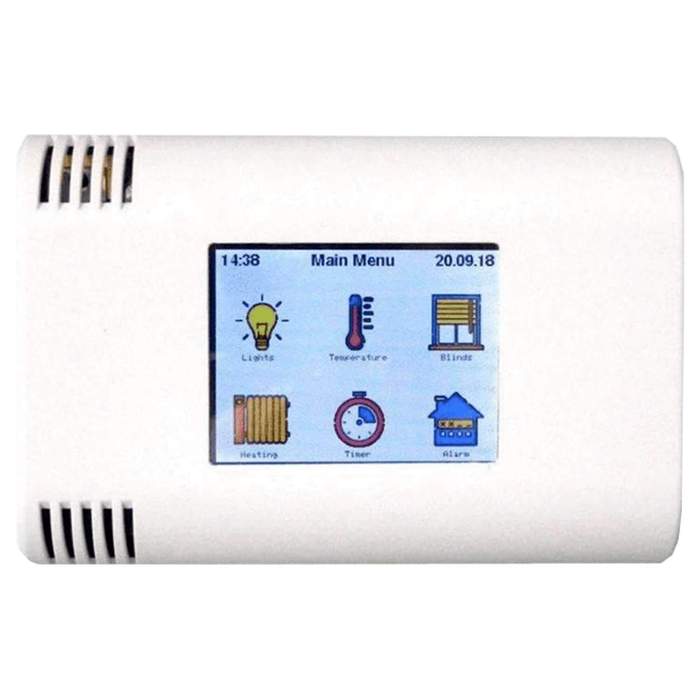
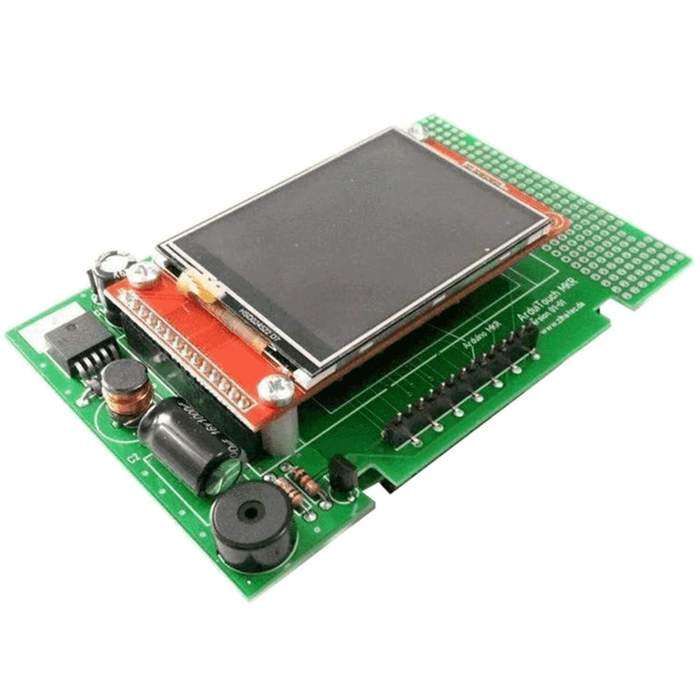
ArduiTouch Wandgehäuse Set für ESP8266 und ESP32
Wandgehäuse 120mm x 80mm x 35mm (W x H x D). 2,4 Zoll (6,14cm) Farb-TFT mit 320 x 240 Pixeln (ILI9341). Resistiver Touchscreen (Touchcontroller XPT2046) Integrierter 5V Spannungsregler (Eingangsspannung 9 - 35V DC). Eingebauter Piezosummer.
https://www.az-delivery.de/blogs/azdelivery-blog-fur-arduino-und-raspberry-pi/arduitouch-wandgehaeuseset-mit-touchscreen-fuer-esp32-und-esp8266
https://www.hwhardsoft.de/english/projects/arduitouch-esp/
NodeMCU und ESP8266 – Einstieg in die Programmierung
https://www.mikrocontroller-elektronik.de/nodemcu-esp8266-tutorial-wlan-board-arduino-ide/
ESP Typen
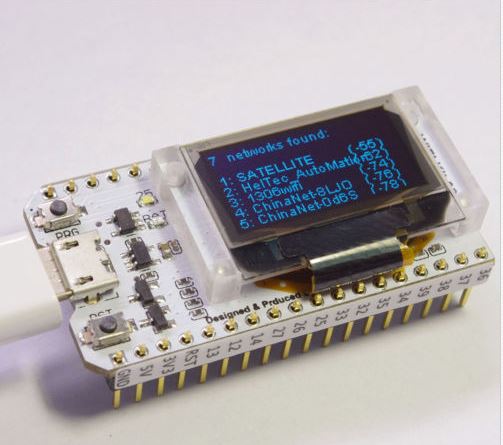
Bluetooth Wifi ESP-32 Entwicklungs Board Modul Lora32 Lora 868Mhz Esp32 Lor M5J7
Hauptmerkmale: SX1276-Chip basierend auf ESP32-WLAN, 868 - 915 MHz-Frequenz, hohe Empfindlichkeit über -148 dBm, + 20 dBm Ausgangsleistung, hohe Zuverl? ssigkeit, lange übertragungsdistanz Integrierte 32 MB Flash-Wi-Fi-Antenne, 0,96-Zoll-Blau-OLED-Display, Lithium-Batterie-Ladeschaltung, CP2102-Schnittstelle und serieller USB-Chip, perfekte Unterstützung für die Arduino-Entwicklungsumgebung, kann für die Programmprüfung verwendet werden, die Produktentwicklung ist sehr einfach und schnell Spezifikationen: Betriebsspannung: 3,3 - 7 V Betriebstemperaturbereich: -40 bis 90 ℃ (-40 bis 194 ° F) Unterstützung für Sniffer-Softwareprotokollanalyse-, Stations-, SoftAP- und Wi-Fi Direct-Modi Datenraten: 150 Mbps bei 11n HT40, 72 Mbps bei 11n HT20, 54 Mbps bei 11 g, 11 Mbps bei 11b Sendeleistung: 19,5 dBm bei 11b, 16,5 dBm bei 11 g, 15,5 dBm bei 11n Empf?ngerempfindlichkeit bis -98 dBm Durchgehender UDP-Durchsatz: 135 Mbps Farbe: schwarz Material: Metall + PC Lieferumfang: 1 * Bluetooth WIFI ESP-32 Entwicklungsboard-Modul Erinnerungen:
1) Die 868/915 MHz Antenne muss mit der IPEX-Schnittstelle verbunden sein (wenn die Antenne nicht angeschlossen ist, kann dies den LoRa-Chip besch?digen) 2) Wenn der Akku voll ist, funktioniert die blaue LED nicht mehr. 3) Achten Sie bei der Verwendung auf das Plus und Minus der Batterie, da diese sonst bescädigt wird. 4) Beim Touchscreen-Eingangssignal des IO-Ports müssen Sie den 100nF-Pull-Down-Kondensator zu diesem Pin hinzufügen.
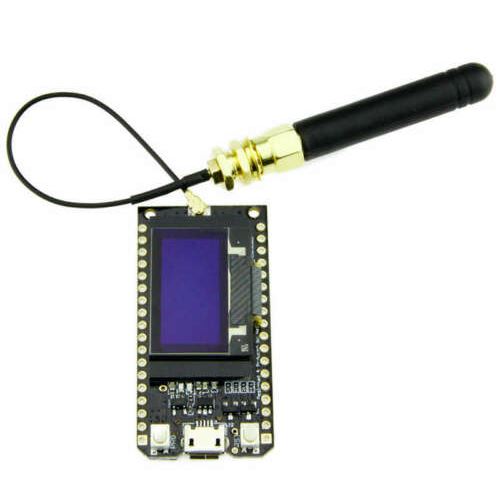
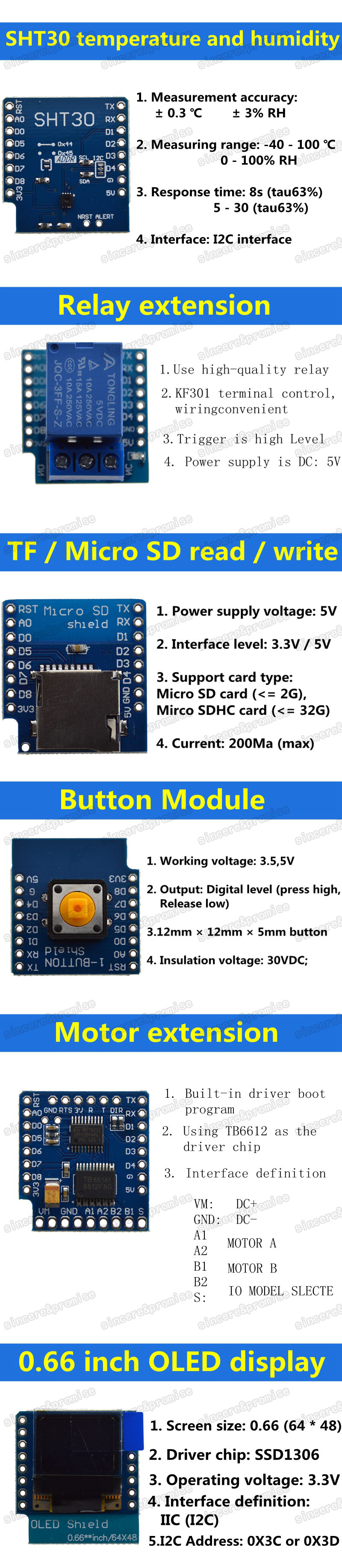
ESP32 WIFI chip 0.96 inch OLED Bluetooth WIFI Kit CP2102 32M module for arduino
WIFI Kit 8 is developed by our company cost-effective Internet of things development program, the main chip using ESP8266, with CP2014USB to serial chip, lithium battery interface and charge and discharge circuit, 32MByte Flash, WIFI antenna, 0.91-inch OLED display.
Can be programmed in Ard uino and NodeMCU environments. Operation is consistent with NodeMCU.
Leads all pins of ESP8266 12 digital pins can be configured to read, write, IIC, SPI, the middle, PWM and other functions 1 AD input Integrated 0.91-inch 128 * 32 OLED Working voltage: 3.3V ~ 7V